The European Union continues to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases it produces. According to statistics, in 2023 it amounted to 3.4 billion tons, which is 5.1% less than in 2022.
Reuters writes about this with reference to Eurostat data.
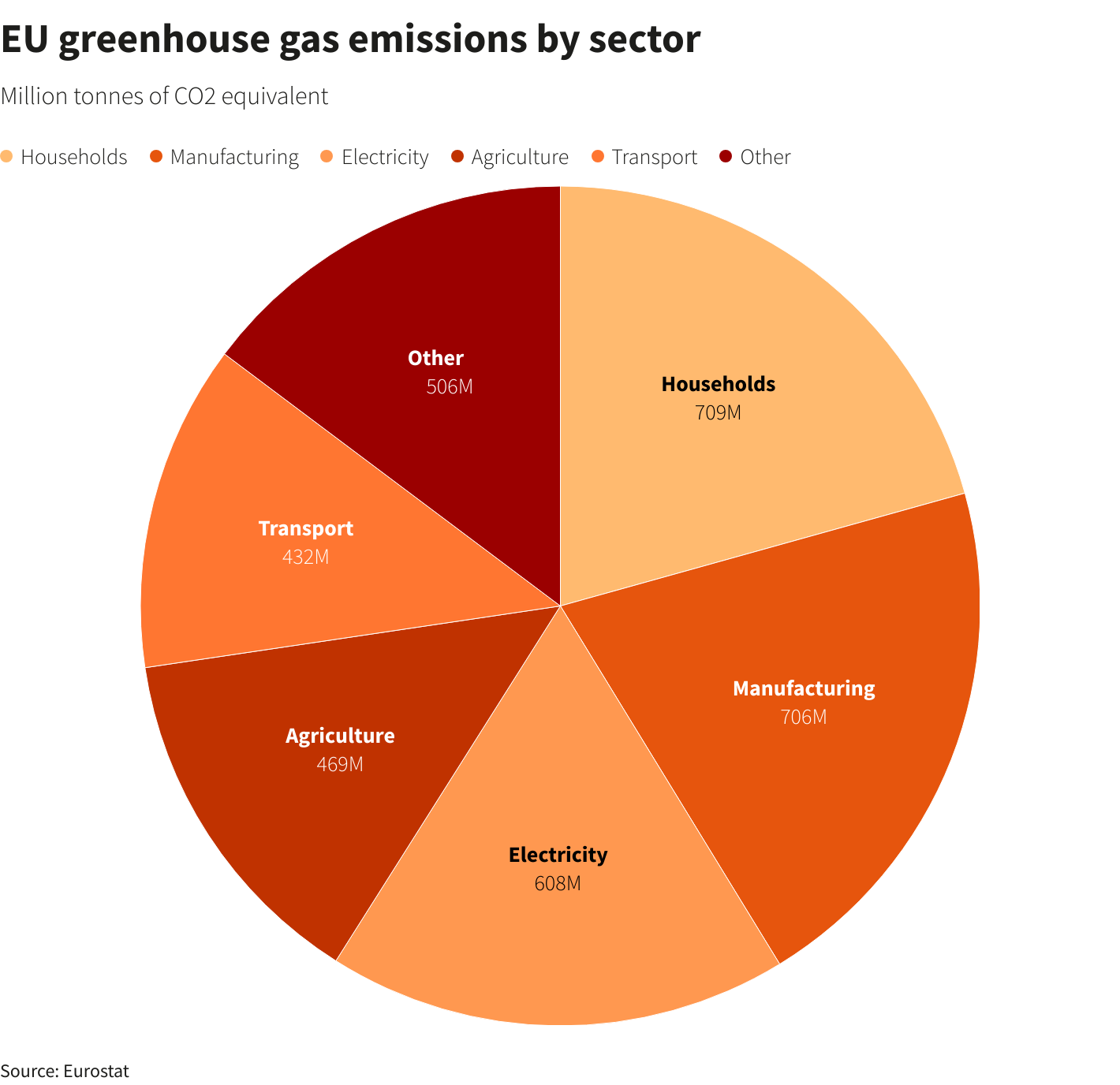
A comparison of the total amount of greenhouse gases generated in 2022 and 2023 in the EU, as well as the share of each sector in it, is shown in the diagram below.
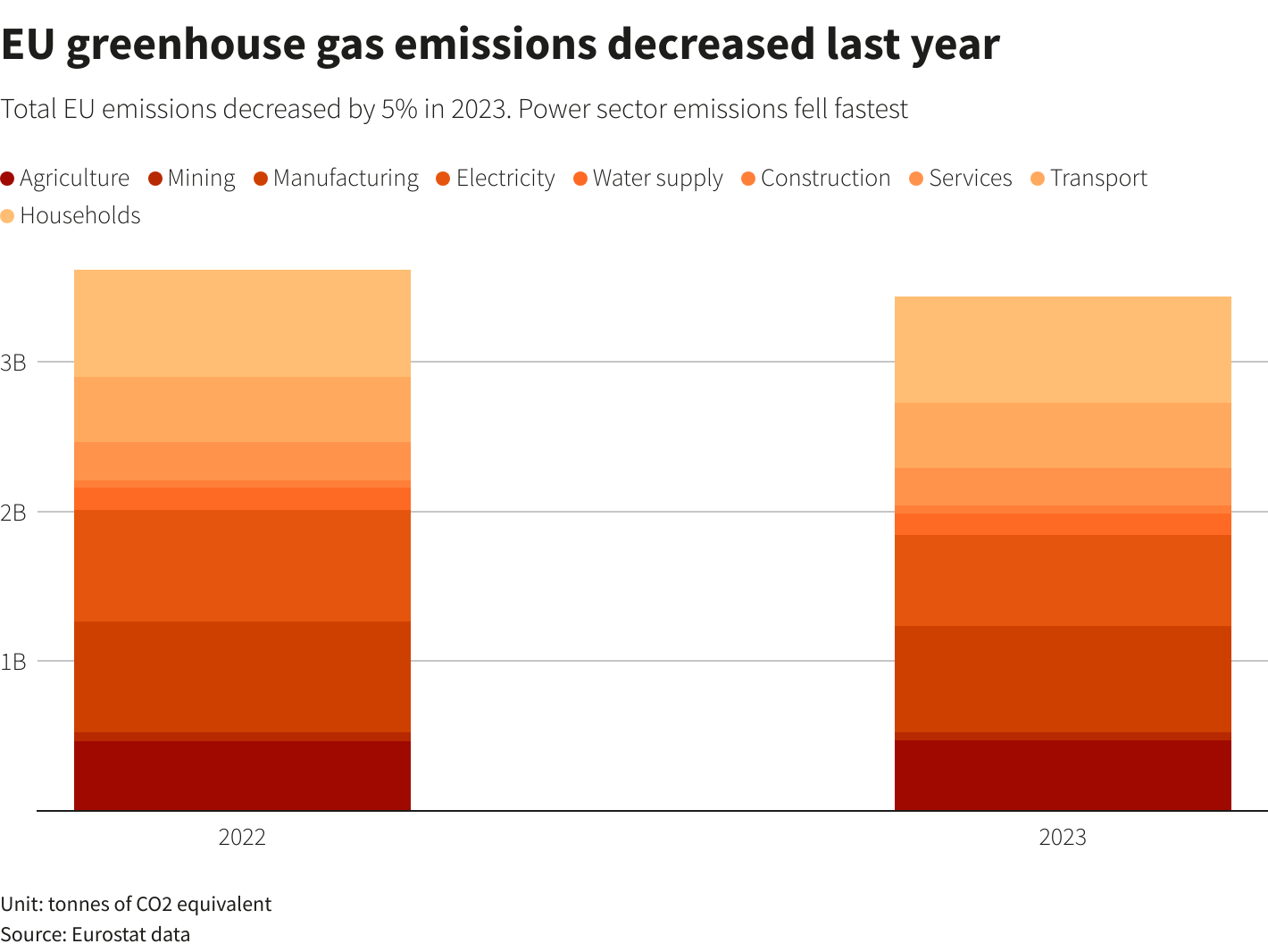
The amount of emission reduction depends on the sector. Yes, emissions from electricity generation are falling the fastest, and this sector is on track to meet the EU's climate goals. Emissions from electricity, gas, steam and air-conditioning production have fallen by around 18% thanks to a shift to more renewable energy.
Overall electricity demand also fell due to lower industrial production and mild weather.
Other sectors are lagging behind. Emissions from transport, construction and mining remained largely unchanged last year, while emissions from agriculture rose slightly.
As a reminder, the EU has committed to reducing net greenhouse gas emissions by 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
In April, EcoPolitic reported that in 2023, the level of greenhouse gases in the air will reach record levels.
EcoPoliticsalso informed that greenhouse gas emissions in Great Britain decreased by 5.4% in 2023.
In April, less than a quarter of electricity in the EU was produced at the expense of fossil fuels.





