Geoptospatial data specialist Adam SamingGton has developed a map that reflects the ratio of the surface of the world covered with trees of trees, and not green areas based on.
To do this, he used satellite images of Modis sensors on Terra satellite, Visual Capitalist reports.
It is noted that forests occupy about 31% of the earth's surface and absorb about 15.6 billion tons of carbon every year. Most of the trees are found in boreal, ie northern, forests of Russia and Canada, the tropical forests of the Amazonia in South America and coniferous and deciduous forests of China.
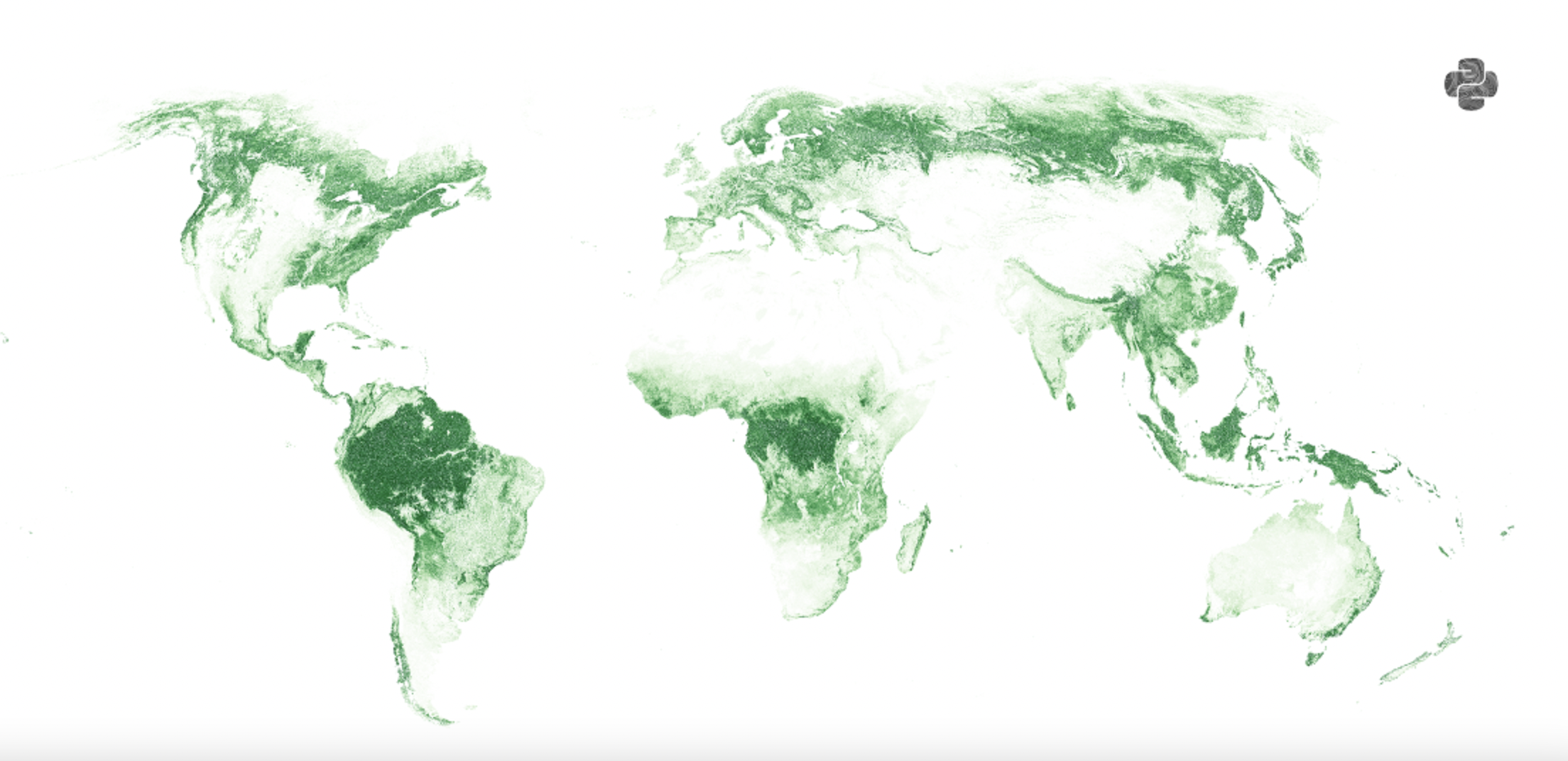
You can view the map in higher resolution at the link.
Asia
The article emphasized that Asia has one of the richest and most diverse green covers in the world. Thus, in Russia, a fifth of the world's trees are concentrated on an area of 815 million hectares, which also extend to the European continent.
The authors noted that China is the fifth greenest country in the world, and the area of its forests reaches 220 million hectares.
"In 1990, China's forests occupied only 157 million hectares, which was 16.7% of the country's territory. By the end of 2020, this forest cover had reached 23.4% thanks to decades of greening efforts,” they said.
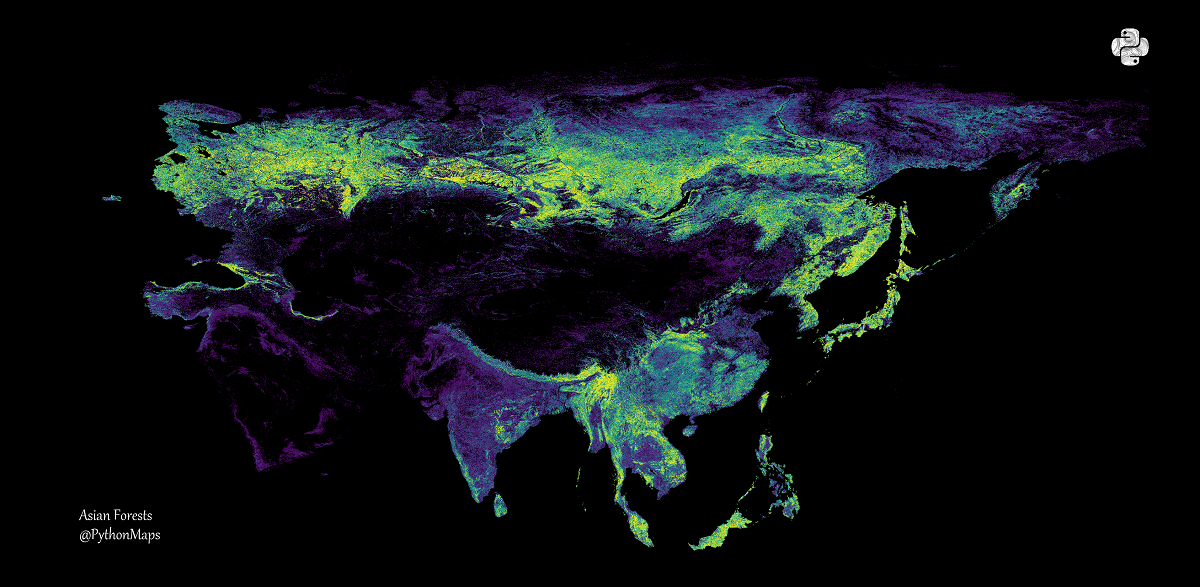
The article emphasized that the third most biodiverse country on the continent — Indonesia — is losing its green cover. The area of the country's forests reaches 92 million hectares, and 10-15% of the world's known plants, mammals and birds live on its territory.
"Unfortunately, over the past 50 years, 74 million hectares of the country's tropical forests have been cut down, burned or degraded," the authors emphasized.
Amazon and Congolese tropical forests
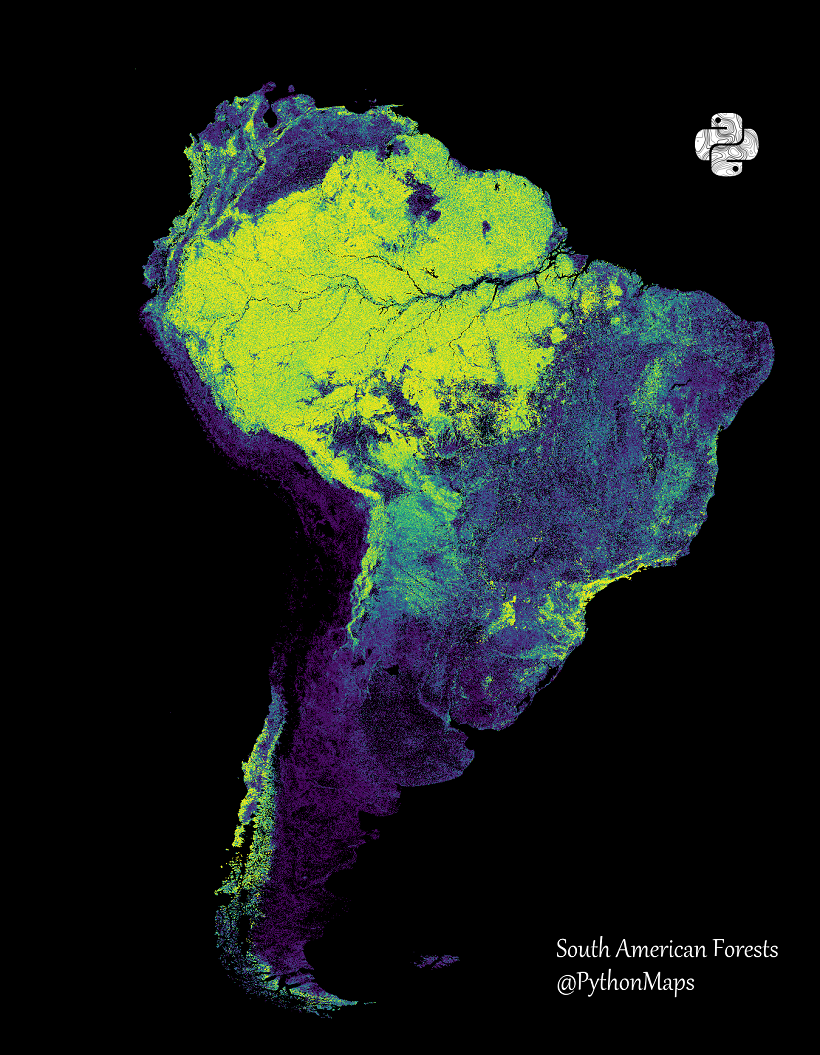
It is noted that in South America, Brazil has the second largest green cover in the world, and the Amazon rainforest covers an area of 497 million hectares.
"The Amazon rainforest, one of the most diverse places on the planet, is believed to contain about 10% of the world's biodiversity," the authors said.
They added that the tropical moist broad-leaved forests of nine countries in central Africa are one of the world's regions that absorb more carbon than they emit. These are the tropical forests of Congo.
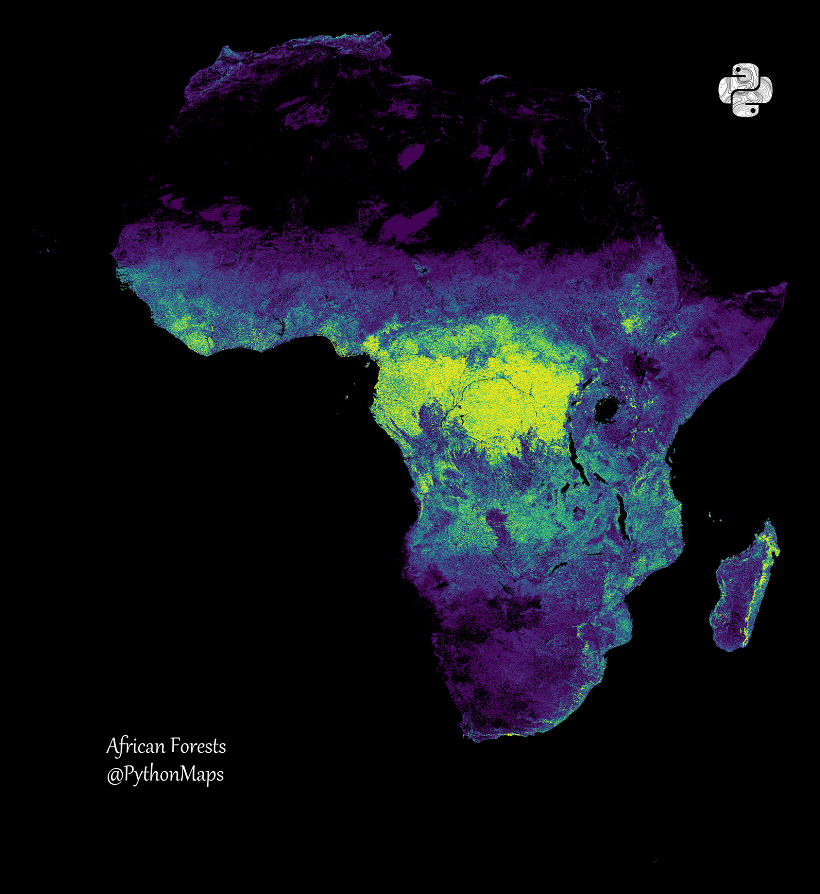
Forests of North America
There are 723 million hectares of global forests on the territory of Canada, the USA and Mexico.
"The vast expanses of pine and fir in the Great White North, combined with the mixed forests of the United States, make the continent one of the largest carbon sinks in the world," the article said.
It is noted that Canada has 347 million hectares of forests, which makes it the third greenest country in the world. About 40% of Canada is covered with trees, accounting for 9% of the world's forest cover. And its boreal forests store twice as much carbon per unit as tropical forests.
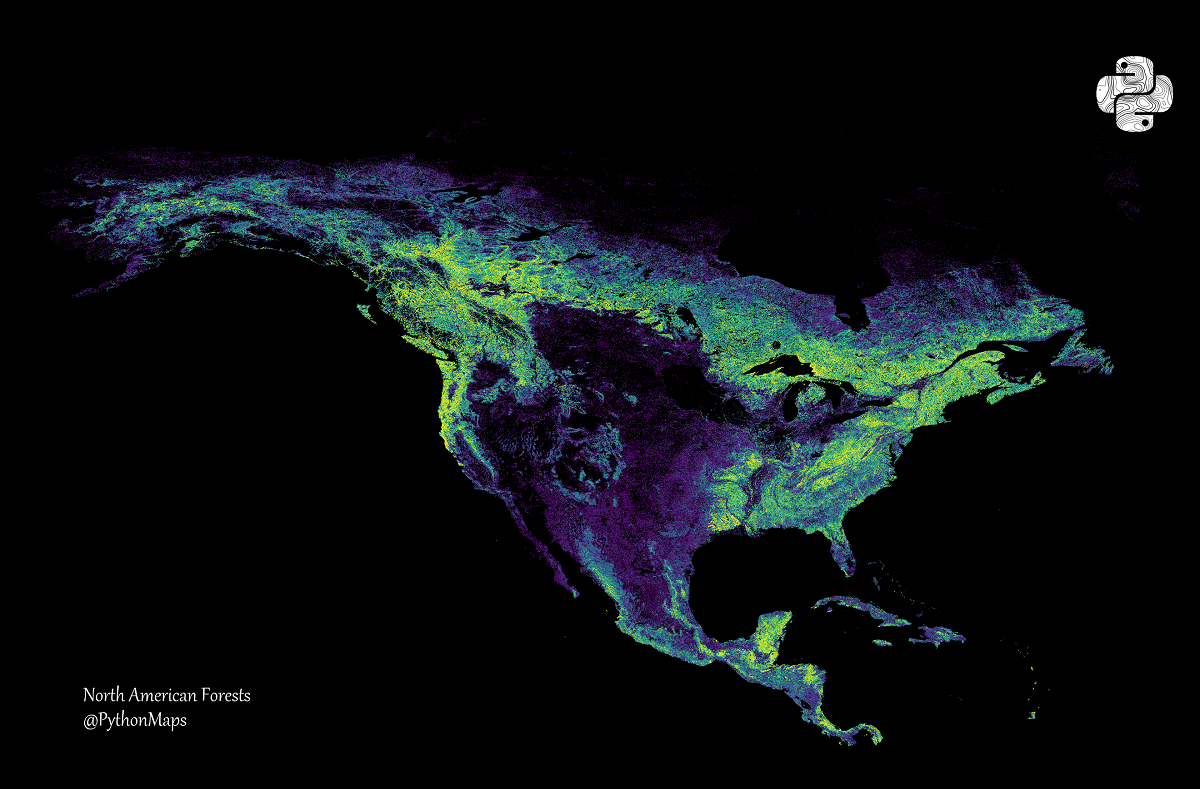
The authors said that the US has approximately 8% of the world's diverse forests, located on 310 million hectares of land. In the USA there are boreal forests of Alaska, pine plantations, deciduous, coniferous and tropical forests.
Lost forests
Symington used data from the University of Maryland to track changes in global forest cover from 2000 to 2021 to show the scale of deforestation, it said. Thus, since 2000, 104 million hectares of forests have been cut down in the world, in particular, in 2020, more than 10,000 km2 of Amazon forests were destroyed for the construction of roads.
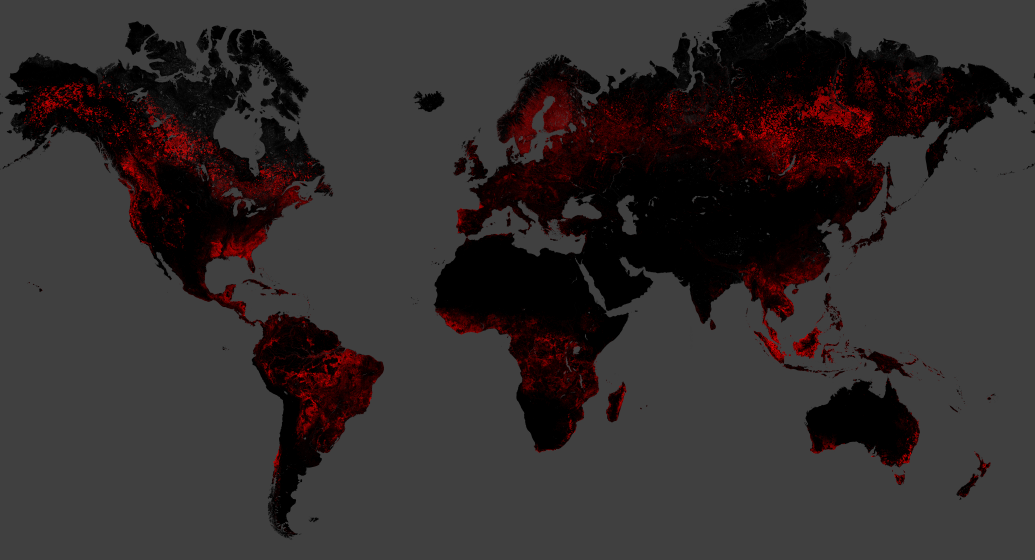
The authors emphasized that in addition to direct destruction, forests also suffer from the effects of climate change, namely droughts, fires, hurricanes, alien species, etc.
They emphasized that at the UN Conference on Biodiversity (COP15), held in Montreal in 2022, the countries of the world undertook to adhere to the "30X30" plan, which envisaged the preservation of the world's terrestrial and marine ecosystems by 2030.
"There is still hope for the world's forests," the article noted.
As EcoPolitic reported earlier, in 2021 Earth, mainly due to logging and fires, lost 11.1 million hectares of tropical forests.





