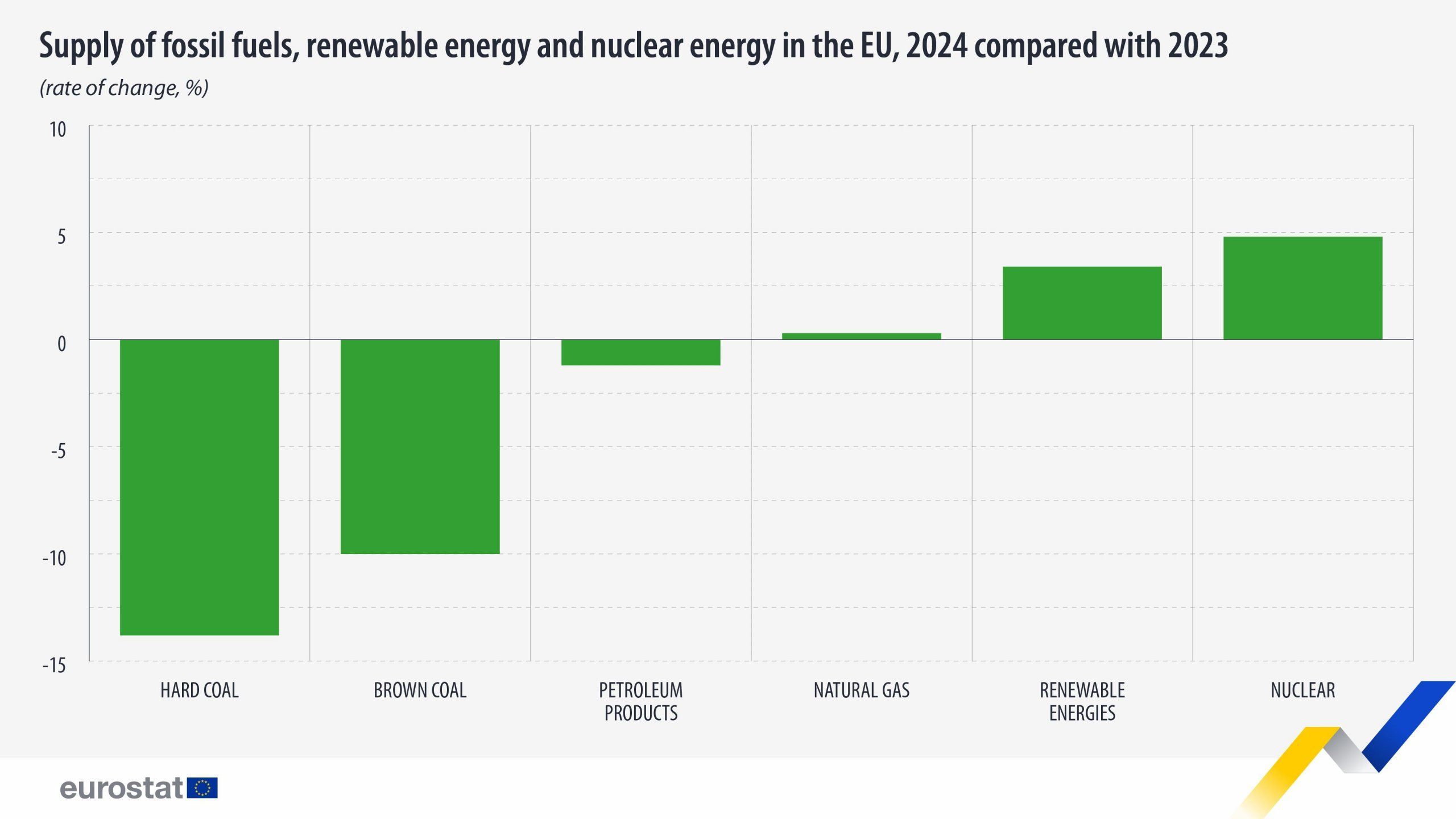
According to preliminary data, in 2024, renewable energy supply in the European Union increased by 3.4% compared to 2023, reaching 11.3 million TJ, and accounted for 47.3% of the electricity produced in the bloc's countries.
This was reported by Eurostat.
In contrast, coal supply continued to decline. Lignite supplies fell by 10% to 199,302 thousand tons, and hard coal supplies fell by 13.8% to 110,924 thousand tons. Both figures are the lowest ever recorded.
After a sharp drop in natural gas supplies to the EU in 2023, 2024 saw a very modest increase of 0.3% compared to 2023. It reached 12.8 million TJe.
Supplies of oil and petroleum products amounted to 454,038 thousand tons. This figure shows a decrease of 1.2% compared to 2023.
Supplies of fossil fuels, renewable energy, and nuclear energy in the EU in 2024 compared to 2023
Source: ec.europa.eu.
Electricity production
In 2024, renewable energy sources (RES) were the leading source of electricity in the EU, accounting for 47.3% of total production. They generated 1.31 million GWh, which is 7.7% more than in 2023.
Conversely, the amount of electricity generated from fossil fuels decreased by 7.2% compared to the previous year. It amounted to 0.81 million GWh, or 29.2% of total electricity generation.
Nuclear power plants generated 0.65 million GWh, or 23.4% of total electricity production in the EU. Compared to 2023, production at these power plants increased by 4.8%.
Electricity production in the EU from 1990 to 2024

Source: ec.europa.eu.
Recently, EcoPolitic wrote that in 2024, the world set a new record for electricity demand and CO2 emissions.





