In Ukraine, there are several types of environmental taxes that companies must pay. Most often, the eco-tax is paid for emissions into the atmosphere and discharges of pollutants into water bodies. Currently, the environmental tax rate on CO2 emissions in Ukraine is one of the lowest in the world.
EcoPolitic decided to find out who pays eco-taxes in Ukraine, how much and for what.
Ecological tax is a state-wide mandatory payment that is made for:
- emissions pollutants in atmospheric air stationary sources of pollution. However, in relation to carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, the eco-tax is paid only when their volume exceeds 500 tons per year. There are no such limits for other pollutants;
- discharges of polluting substances directly into water bodies;
- waste placement. The exception is the placement of certain types of waste on their own territories (objects) of economic entities such as secondary raw materials;
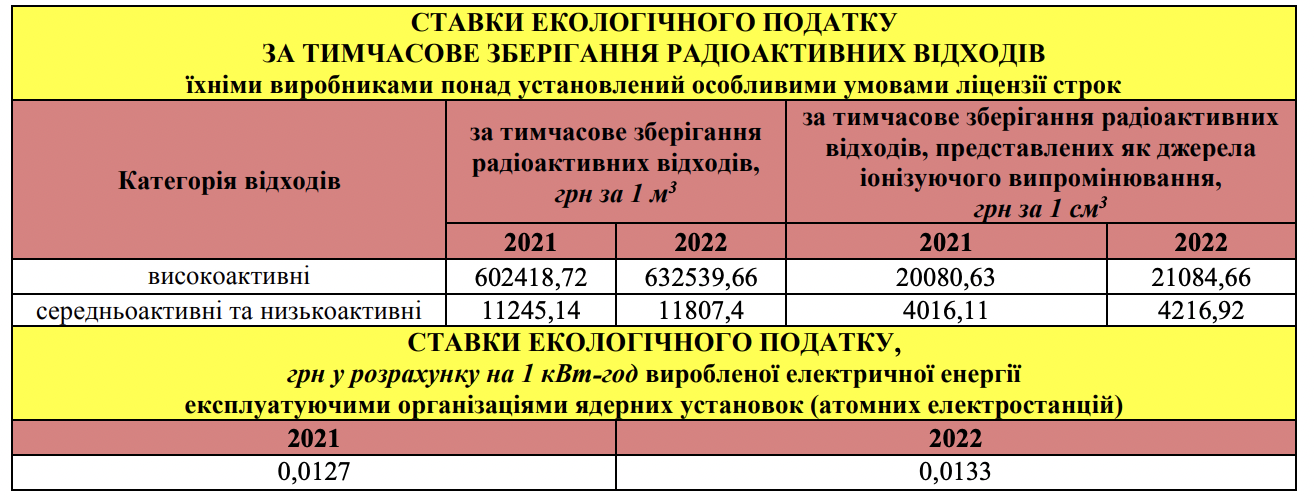
- formation radioactive waste (including already accumulated), as well as their temporary storage at manufacturers beyond the license term.
In general, from January 1 to December 31, 2021 UAH 5.44 billion of eco-taxes were paid.
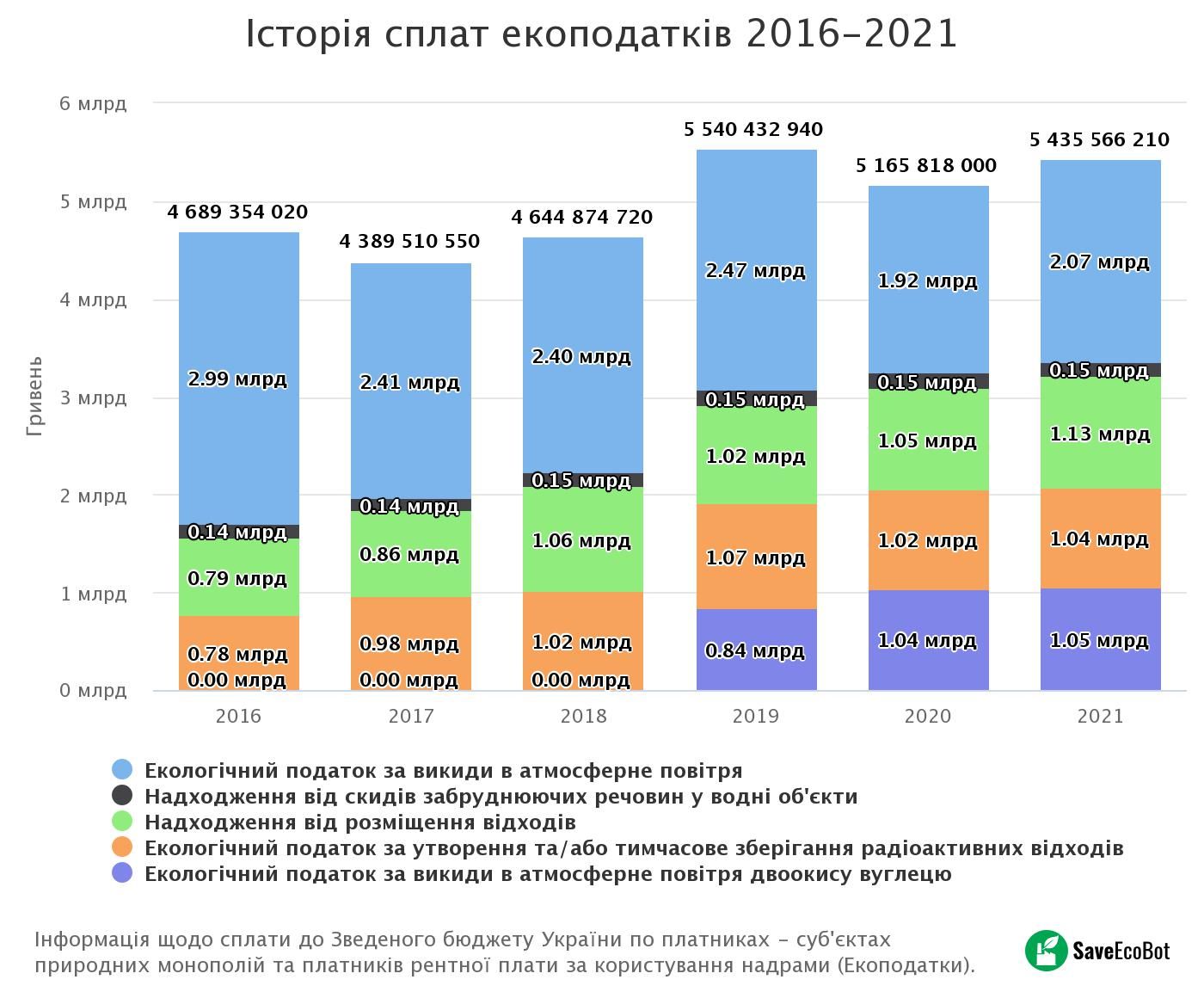
Types of environmental tax and the amount paid to the state budget
**Data for the period from January 1 to December 31, 2021
- Ecological tax for atmospheric emissions — 2.07 billion hryvnias
- Income from disposal of waste — UAH 1.12 billion
- Environmental tax for emissions of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere — UAH 1.05 billion
- Environmental tax for the generation and/or temporary storage of radioactive waste — UAH 1.04 billion
- Revenue from discharges of polluting substances into water bodies — 150.53 million hryvnias

Legal entities are obliged to pay eco-taxes in the case of a stationary source of pollution — an enterprise, workshop, unit, installation or other immovable object that causes pollution in the form of discharges or emissions.
Such a source is not necessarily a real estate object, because they include generators, mini-power stations and gas welding equipment (installations) that work on fuel.
Examples of stationary sources of pollution:
- boiler rooms, heating boilers, in particular pellet boilers, gas columns, etc.;
- welding machines;
- cutting equipment, in particular chainsaws;
- drilling rigs;
- heat generators;
- power plants;
- electric generators and mini-power plants;
- grain dryers;
- lawn mowers
Ecotax is paid by the lessee if stationary sources of pollution are included in the lease, and the lessor pays for stationary sources of pollution for heating a building in which several tenants are located.
The tax is not paid at all, if the owner of the boiler and lessor is not an entrepreneur, because a natural person cannot be a payer of eco-tax
However, if the tenant has concluded contracts for the purchase (supply) of fuel for autonomous heating systems (boilers) of rented buildings, tax officials insist that the tenant becomes the payer of the environmental tax.
How the eco-tax is calculated
The calculation is carried out for each pollutant emission separately, and then the total amount is found.
He are calculated independently every quarter based on the actual volumes of emissions, tax rates for formula according to clauses 249.3-249.8 of the PC.
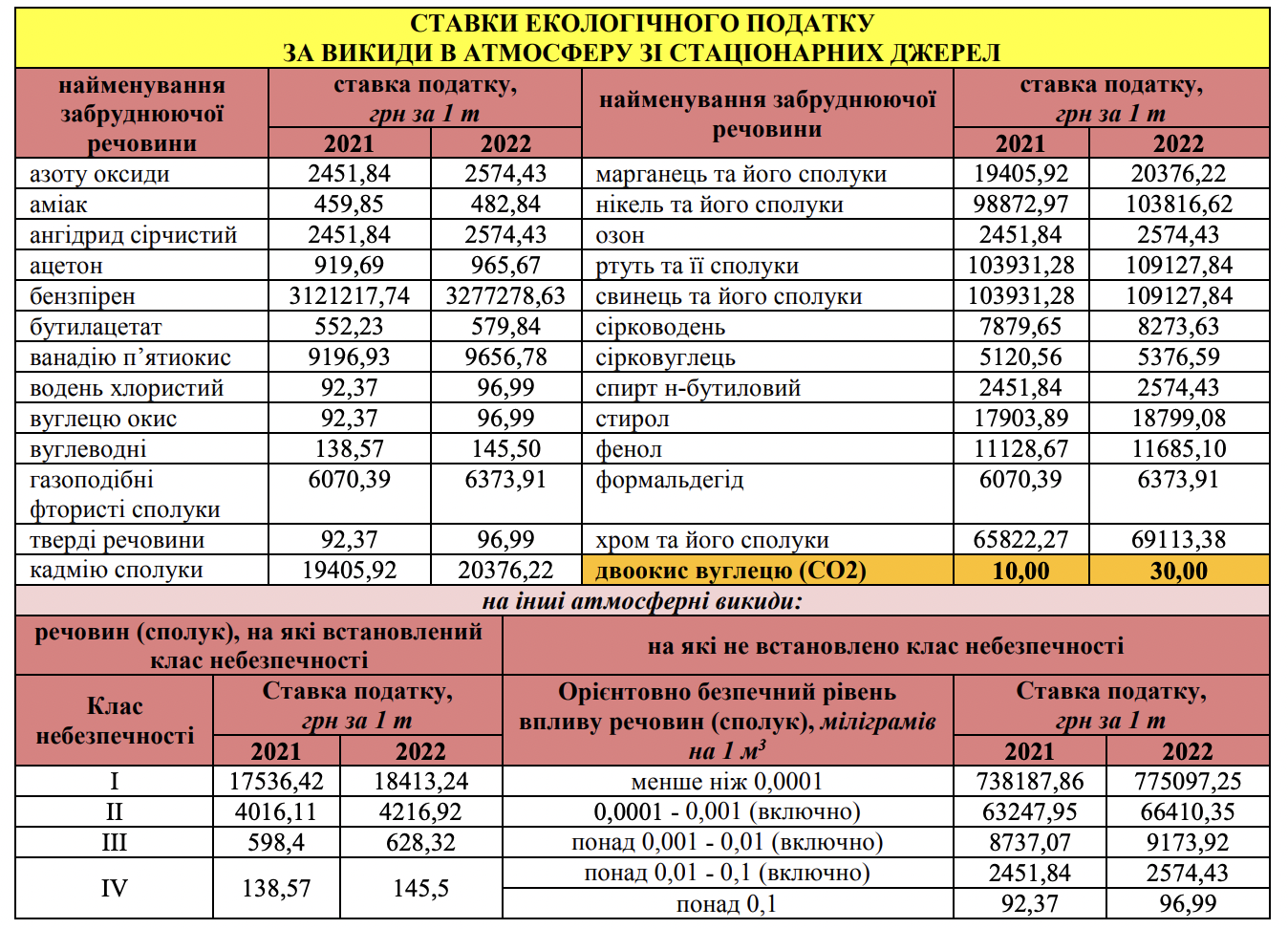
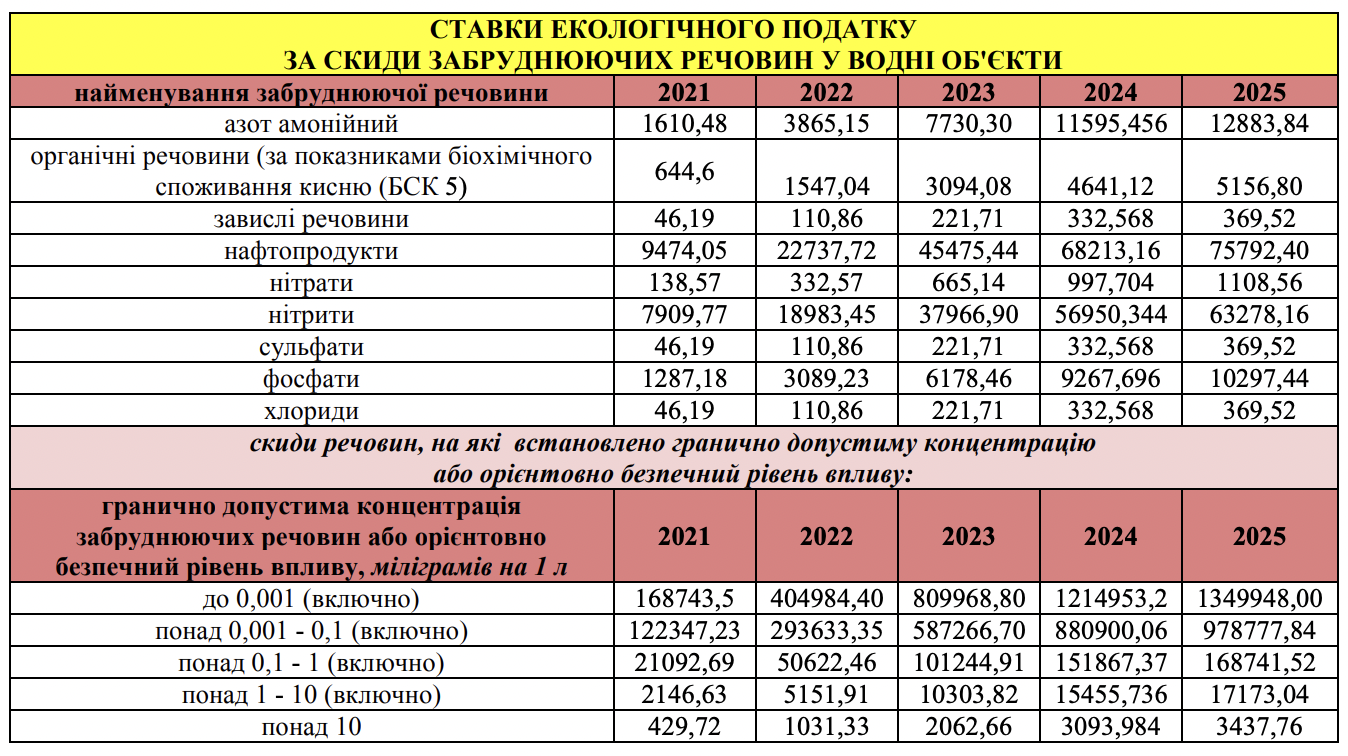
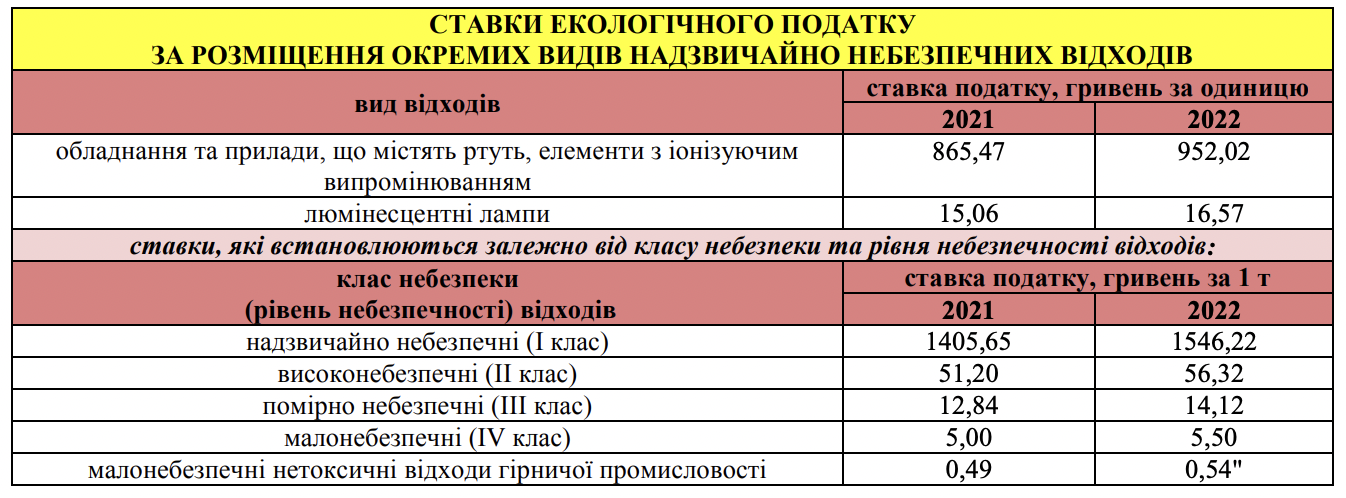
Ecotax under martial law
For the year 2022, enterprises located in the territories of hostilities will not be charged and do not need to pay an environmental tax.
The list of territories on which hostilities are (were) conducted or temporarily occupied by the armed formations of the Russian Federation is determined by the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine, but it has not yet been approved.
As EcoPolitic reported earlier, it became known how much air emissions will cost according to the eco-tax for 2022.





