Asia holds the lead in terms of both the amount of energy generated from renewable sources and the amount of electricity produced from biomass. The leading country both in the region and in the world is China, which has produced more than 25% of the world's electricity from biomass.
Such data was published by the World Bioenergy Association (WBA) in its annual report “Global Bioenergy Statistics. 11th edition. 2024”.
The analysts focused on the global development of energy production from biomass and provided data on all sectors of bioenergy: liquid biofuels, biogas, pellets, forestry, agriculture, waste, etc.
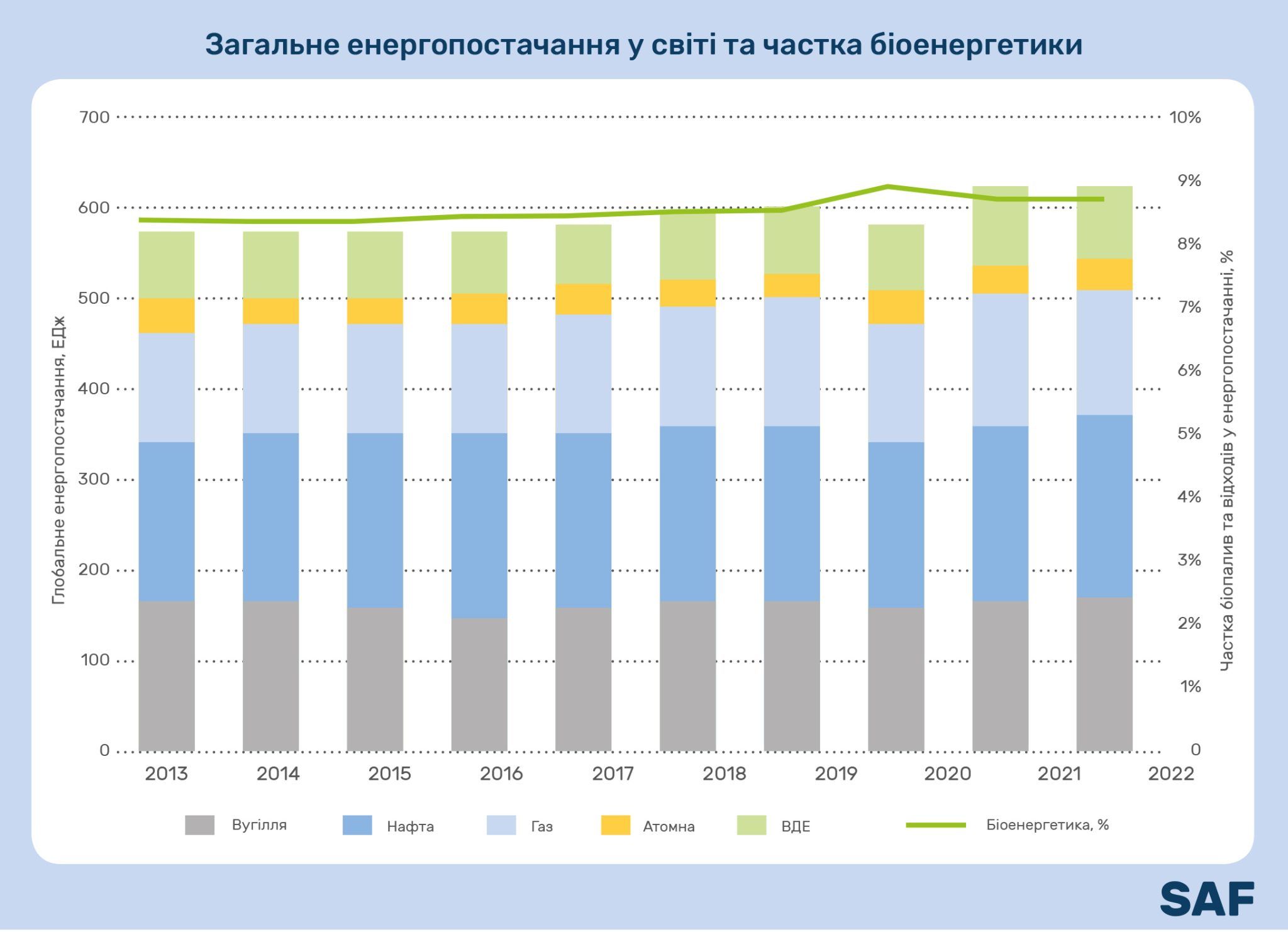
In 2022, renewable energy sources (RES), including biofuels, continued to grow steadily and provided 89 EJ of energy. This is almost 30% more than in the last decade. Bioenergy remained stable at about 9% of the total energy supply.
The share of electricity generated from biomass amounted to 8% of the total from renewable sources. This equals 697 TWh of electricity.
Source: saf.org.ua.
The researchers noted that despite the growth of bioenergy, its relative share remains stable, as wind and solar power have also developed rapidly over the past decade.
Leaders in terms of energy from RES
In 2023, the top three regions of the world with the highest indicators looked like this:
- Asia – 46% (4,087 TWh);
- America — 28% (2,505 TWh);
- Europe — 22% (1,942 TWh).
If we talk about the amount of electricity from biomass, then the distribution is a little different:
- Asia – 51% (357 TWh);
- Europe – 28% (198 TWh);
- America — 19% (133 TWh).
Source: saf.org.ua.
Generation of electricity from biomass
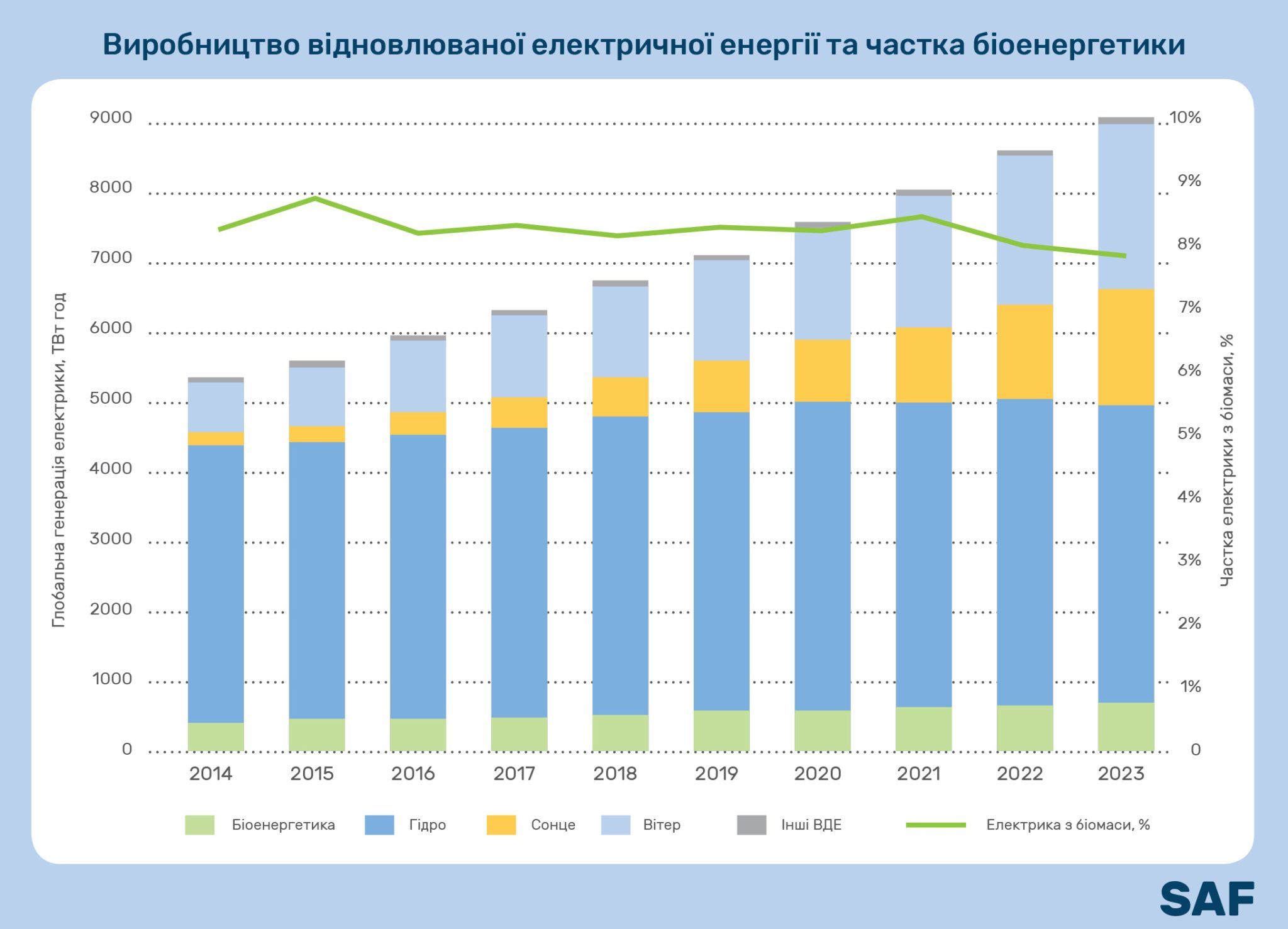
From 2014 to 2023, the production of electricity from biomass showed a 1.6-fold increase – from 439 to 697 TWh.
Analysts note that over the past decade, Asia's share in global generation has grown from 28% to 51% and reached 357 TWh. Such dynamics allowed it to overtake Europe.
At the same time, America saw a slight decrease from 146 TWh to 133 TWh. Africa and Oceania remain relatively stable – about 7-8 TWh.
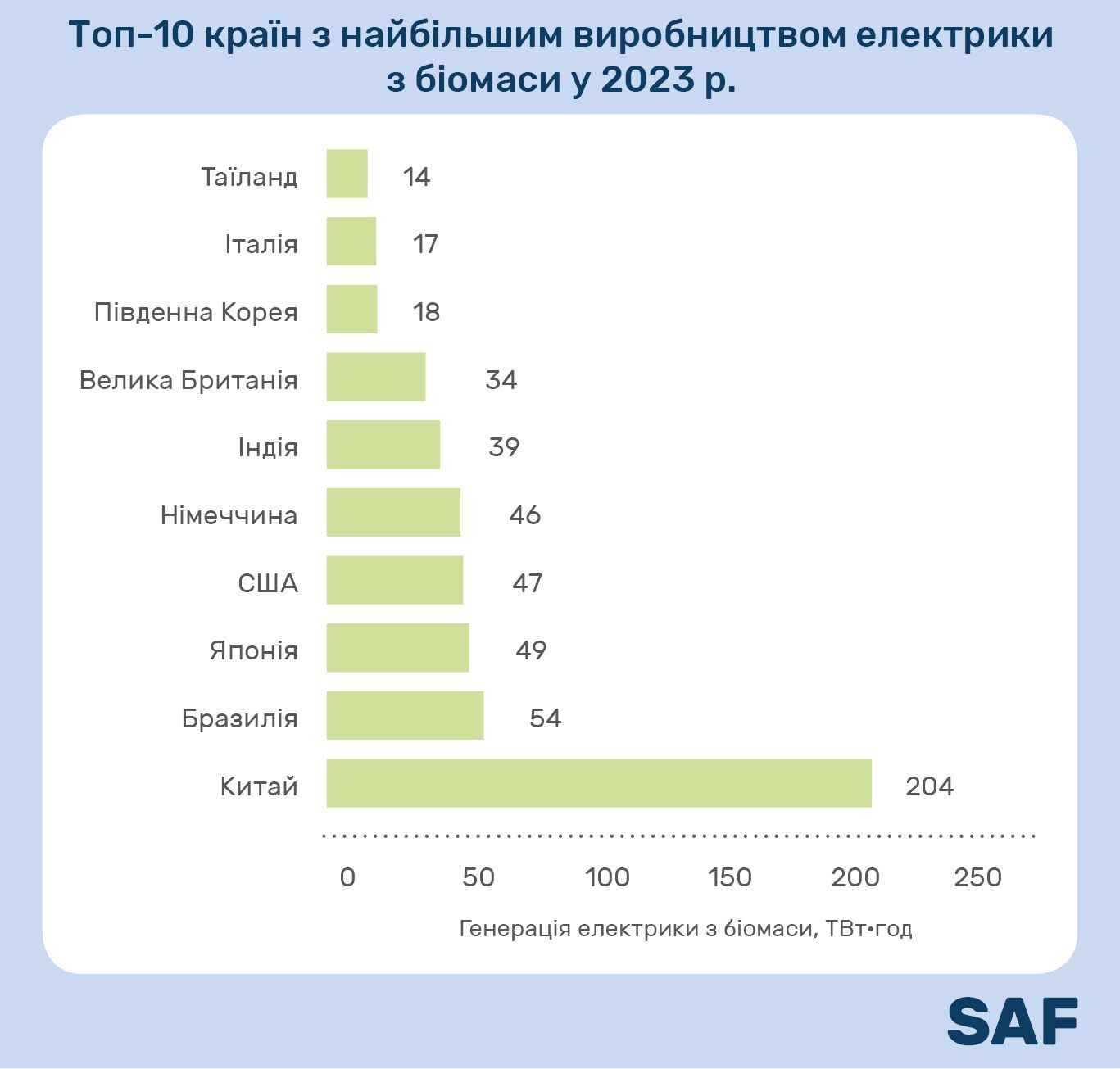
The list of the 10 leading countries with the largest production of electricity from biomass in 2023 is as follows:
Source: saf.org.ua.
In 2023 China produced more than 25% of the world's electricity from biomass – 204 TWh. Record production was achieved in Brazil – 54 TWh. All thanks to 637 biomass projects across the country.
The third place in terms of electricity from biomass was taken by Japan. The country showed the highest growth rate – by 18% compared to the values of 2022.
WBA researchers say that in 2023, bioenergy will make a significant contribution to the production of electricity in European countries. They give the following figures:
- in Denmark, bioenergy accounted for more than 20% of the total electricity production;
- in Finland, bioenergy accounts for 14% of electricity production;
- in the United Kingdom – 12%.
Thermal energy
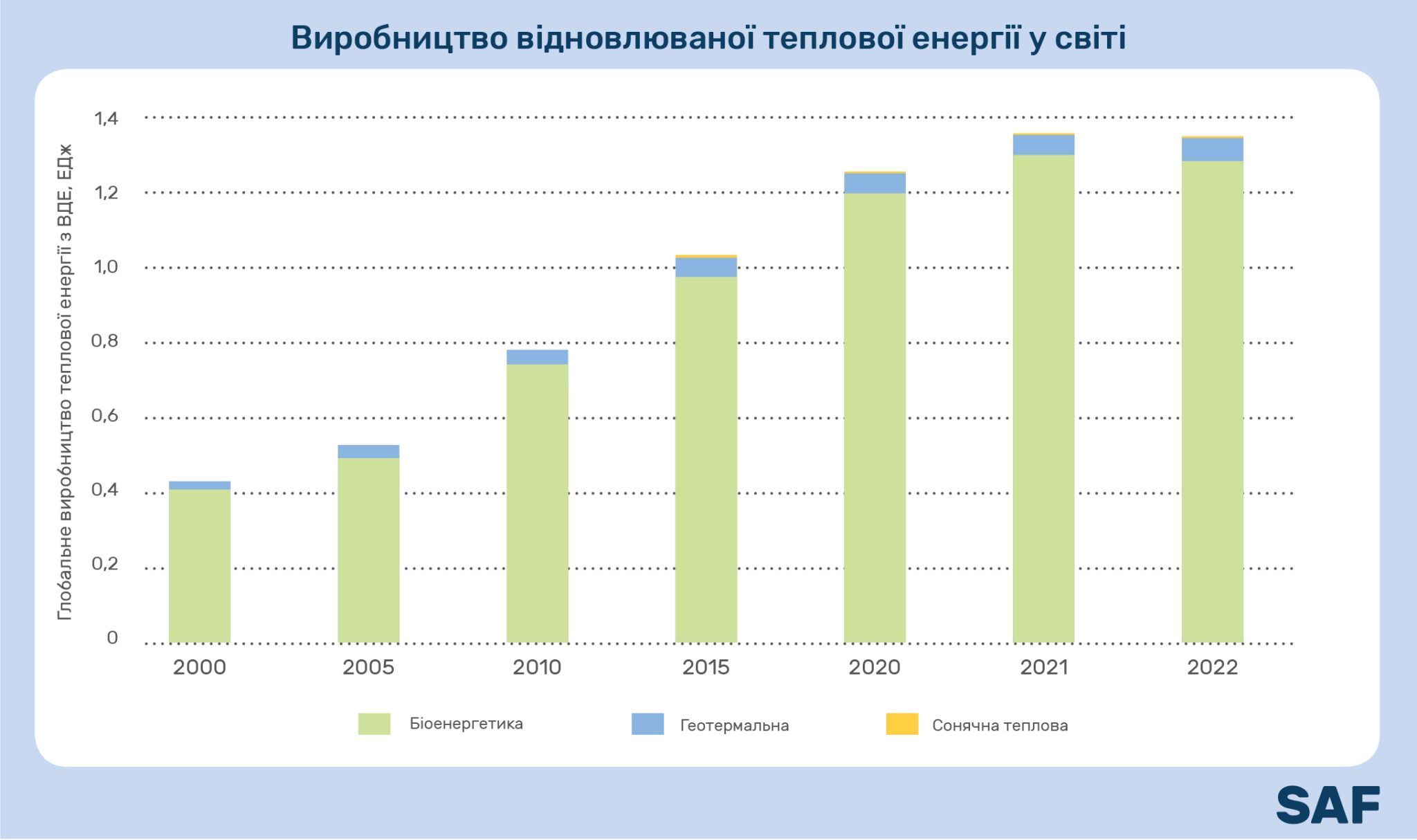
According to the report, biomass provided 96% of all renewable heat produced in 2022. The share of geothermal and solar thermal technologies was quite insignificant. Regionally, Europe produces almost 80% of the world's renewable heat, while bioenergy covers 95%.
Source: saf.org.ua.
Transport
The main players in the field of renewable energy for transportation in 2023 were the United States and Brazil. This year, 6% of the energy used in US transportation came from renewable sources. All of this energy came from biofuels.
In Brazil, in the same year, RES accounted for 22.5% of transport energy consumption, mainly due to ethanol and biodiesel.
In early October, EcoPolitic reported that the first Ukrainian biomethane began to enter the national gas transportation system. It was supplied to the grid by the VITAGRO group of companies together with the specialists of the Khmelnytskyi gas distribution system operator.
A little later, we talked about a legislative initiative – the draft law No. 12058 “On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts on Restoration of Degraded Lands, Stimulation of Energy Plants Growing and Production of Alternative Biofuels”. In particular, it introduces the definition of energy crops into the conceptual framework of the Law of Ukraine “On Alternative Fuels”, etc.





