The Chinese Ministry of Ecology and Environmental Protection has released draft rules for the national carbon market for consultation. According to it, market participants will no longer be able to borrow quotas from future years and will have stricter restrictions on carrying over unused quotas from previous years.
Bloomberg reports with reference to the Ministry.
These steps are aimed at leaving the market with a "small deficit" of allowances, the ministry said in a statement.
China's allowance market started trading in July 2021. In the early years of its operation, a large number of free allowances kept prices low, so Chinese energy companies had few incentives to reduce emissions.
Therefore, the Chinese emissions market has faced criticism for its limited impact on emissions in the world's largest polluter. The reason for this policy was the fact that against the backdrop of rising geopolitical tensions, China prioritized energy security over long-term climate goals.
So, now we can state changes in the country's approach to this issue.
The draft rules, published on July 2, reversed one of the toughest measures in the previous version, a retroactive reduction in emissions permits issued for 2023.
The ministry also set new emissions targets for 2023 and 2024 for more than 2,200 energy companies covered by the mandatory market. Market participants will be required to report on compliance annually rather than biennially.
Also in a separate document, China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment said the rules would not limit power generation, create higher trading profits for the most efficient plants and continue to exempt gas-fired power plants from paying emissions. The department added that they will compensate peak capacities for being in standby mode, and also exclude indirect emissions from the purchased electricity to avoid accounting complications.
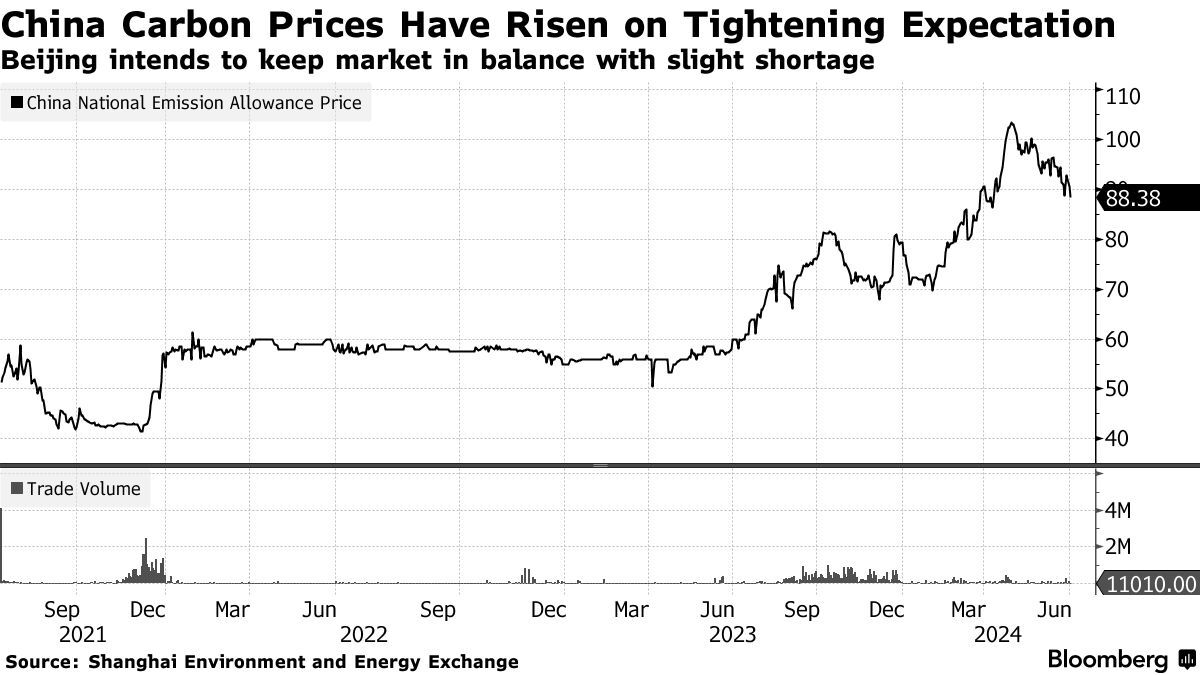
Quota prices in China have risen since February on expectations of policy tightening and the introduction of an earlier-than-expected compliance deadline.
As EcoPolitic previously reported, China plans to implement a carbon footprint management system by 2027.




