For the first time since 2022, greenhouse gas emissions in China showed an annual decline. The 2025 figure was 0.3% lower than the previous year, which is huge for the world's second-largest economy. The reduction occurred despite growing energy demand.
According to CarbonBrief's analysis, emissions fell in almost all major sectors of the economy.
Greenhouse gas emissions from transport fell by 3%, from energy by 1.5%, and from the building materials sector by 7%. On the other hand, emissions from the chemical industry rose by 12%.
"CO2 emissions figures mean that carbon intensity (fossil fuel emissions per unit of GDP) fell by 4.7% in 2025 and by 12% during 2020-25. This is significantly less than the 18% target set for this period by the 14th Five-Year Plan," analysts note.
Overall, to meet its commitments under the Paris Agreement, China must reduce its carbon intensity by 23% in five years.
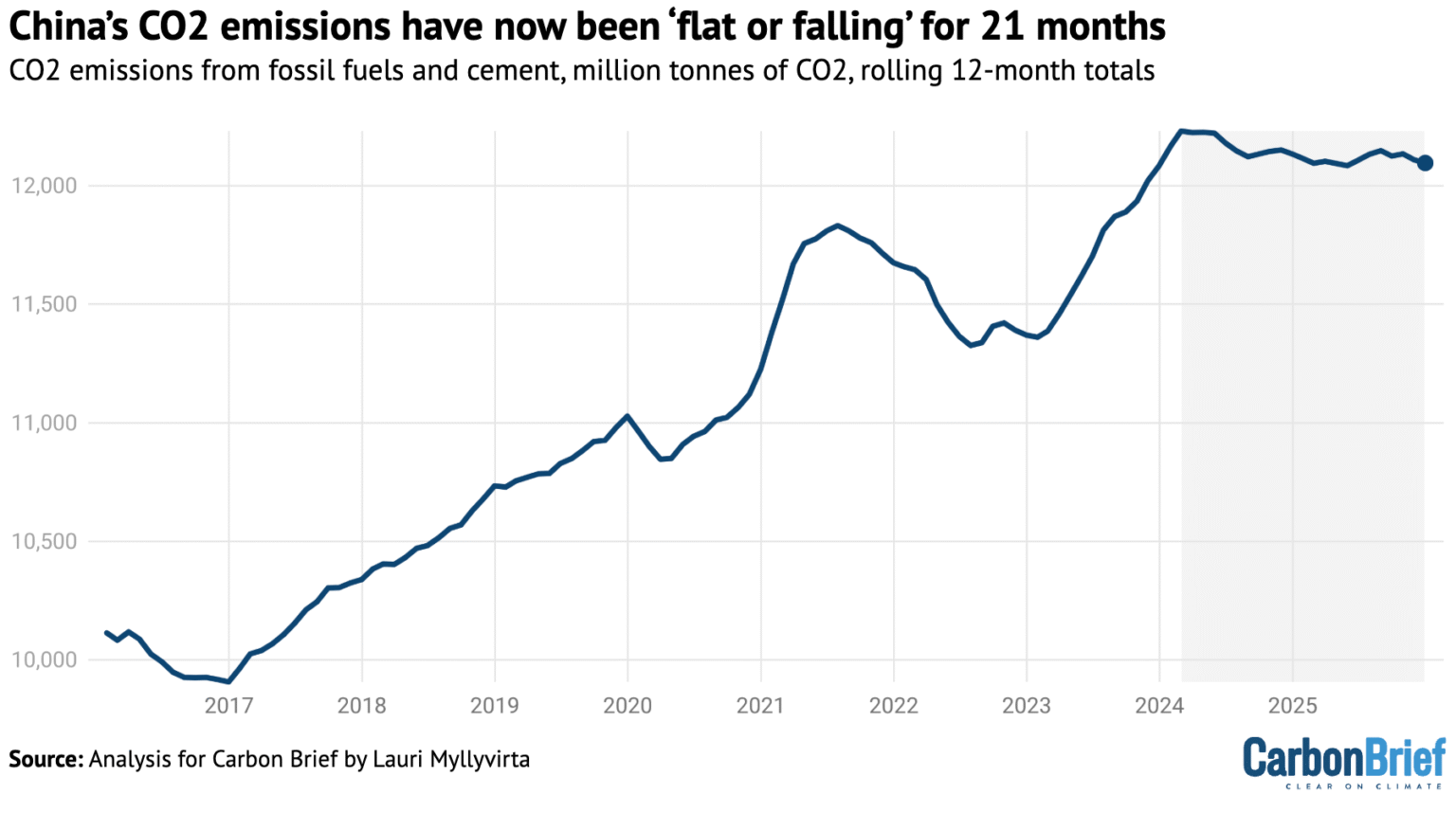
Source: CarbonBrief
The role of clean energy
The largest source of atmospheric pollution in China is the energy sector. However, thanks to renewable energy sources, emissions have been reduced.
Demand for electricity in China in 2025 increased by 520 TWh, but wind, solar, and nuclear energy generated 530 TWh of energy.
The largest increase in new capacity was in solar energy – 360 TWh (43% growth). Wind energy increased its generation by 130 TWh, which is 14% more than in 2024. Nuclear energy grew by 40 TWh and 8%. Energy production from other "clean" sources also increased – hydropower (3%) and bioenergy (3%). All this contributed to a 1% decrease in fossil fuel generation.
“The events of 2025 continued the trend of clean energy production growing faster than total electricity demand. This trend began in 2023 and is a key reason why emissions in China have remained stable or are declining since early 2024,” writes CarbonBrief.
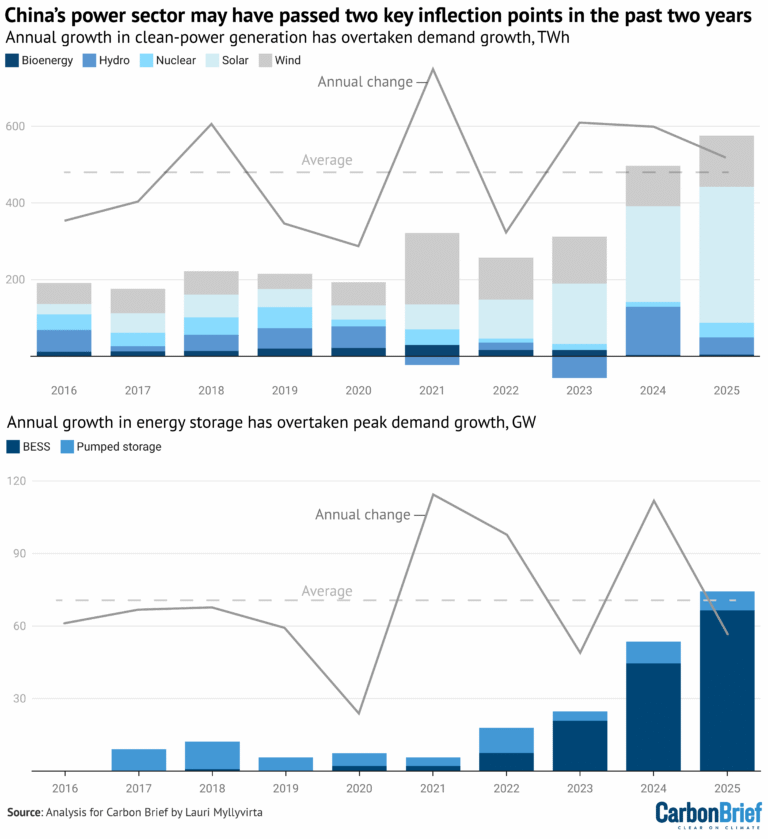
Source: CarbonBrief
Energy storage
At the same time, China is developing a network of energy storage facilities. In 2025, their capacity grew by 75 GW, while peak load increased by 55 GW.
It is the increased volume of energy storage that could allow China to maintain stability in its energy system despite the intermittency of renewables. This may become a key factor in reducing reliance on fossil fuel energy.
EcoPolitic previously reported that China is an undisputed global leader in expanding renewable energy generation capacity. The volume of new solar and wind power projects is three times greater than the total project capacity of all G7 countries combined.





